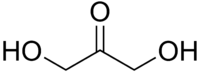
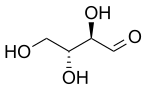
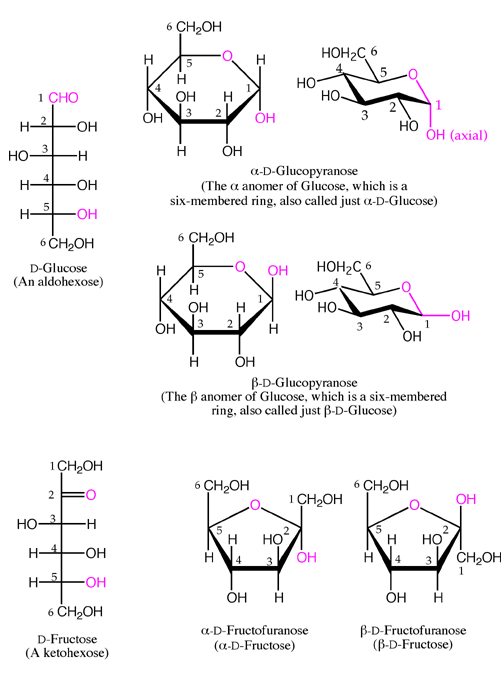
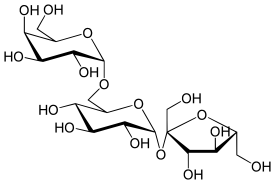
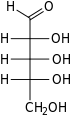
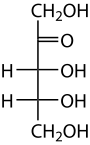
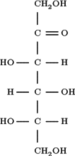
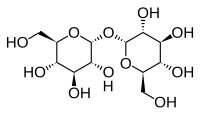
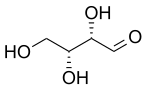
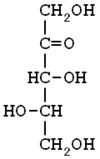
HEMOGLOBINA
Informaçao geral
Textos
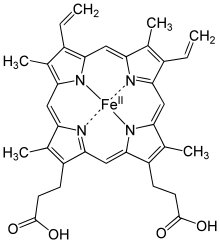
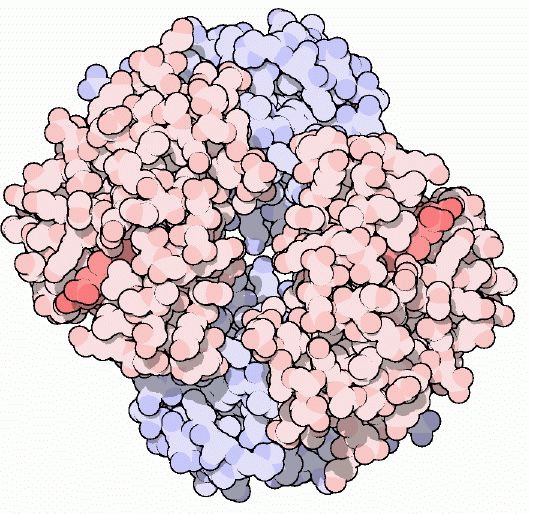
Informaçao especializada
Anemias
Catabolismo do heme



Ciclo de Rapoport-
Luebting
Genes da hemoglobina

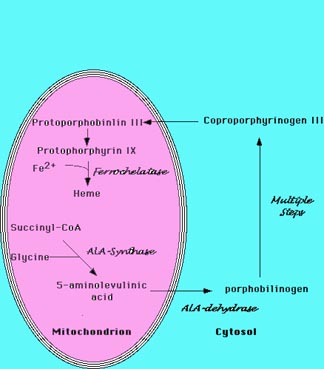
Heme
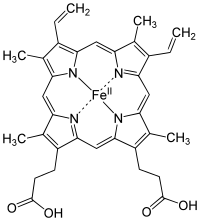


Texto e vídeo
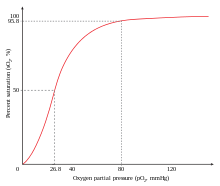
Hemoglobina e
cooperatividade
Hemoglobina
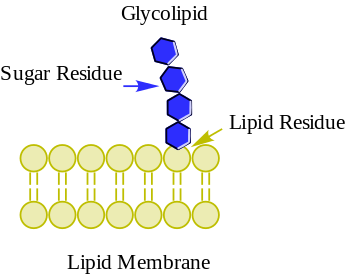
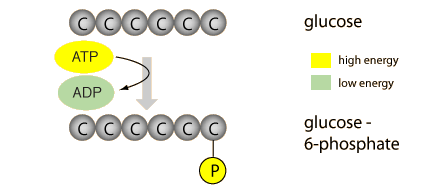
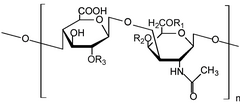
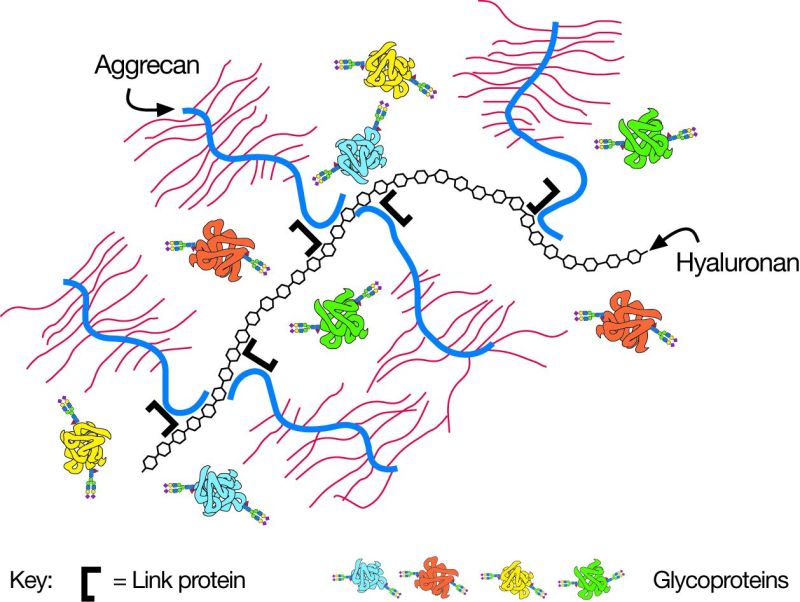
glicosilada
Hemoglobinopatias
Mioglobina


Porfirinas
Porfirias
Sintese do heme